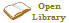Georg Forster
 Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster possibly chosen commemorating the family's ancestors from Yorkshire. The German form of his name is also common in English (for example, Thomas P. Saine's English-language biography is titled "Georg Forster"), which helps to distinguish him from George Forster, a contemporaneous English traveller.}} (; 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German-Polish geographer, naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold Forster, on several scientific expeditions, including James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific. His report of that journey, ''A Voyage Round the World'', contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of Polynesia and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the Royal Society at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature.
Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster possibly chosen commemorating the family's ancestors from Yorkshire. The German form of his name is also common in English (for example, Thomas P. Saine's English-language biography is titled "Georg Forster"), which helps to distinguish him from George Forster, a contemporaneous English traveller.}} (; 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German-Polish geographer, naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold Forster, on several scientific expeditions, including James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific. His report of that journey, ''A Voyage Round the World'', contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of Polynesia and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the Royal Society at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature.After returning to continental Europe, Forster turned toward academia. He taught natural history at the Collegium Carolinum in the Ottoneum, Kassel (1778–84), and later at the Academy of Vilna (Vilnius University) (1784–87). In 1788, he became head librarian at the University of Mainz. Most of his scientific work during this time consisted of essays on botany and ethnology, but he also prefaced and translated many books about travel and exploration, including a German translation of Cook's diaries.
Forster was a central figure of the Enlightenment in Germany, and corresponded with most of its adherents, including his close friend Georg Christoph Lichtenberg. His ideas, travelogues and personality influenced Alexander von Humboldt, one of the great scientists of the 19th century who hailed Forster as the founder of both comparative ethnology (''Völkerkunde'') and regional geography (''Länderkunde''). When the French took control of Mainz in 1792, Forster played a leading role in the Mainz Republic, the earliest republican state in Germany. During July 1793 and while he was in Paris as a delegate of the young Mainz Republic, Prussian and Austrian coalition forces regained control of the city and Forster was declared an outlaw. Unable to return to Germany and separated from his friends and family, he died in Paris of illness in early 1794, not yet 40.
Provided by Wikipedia
1
2
4
5
6
7
9
10
11
12
13
14
15