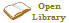Lower Saxony
 Lower Saxony ; ; }} is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people.
Lower Saxony ; ; }} is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people.Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-exclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single ''''. The state's largest cities are the state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Oldenburg, Osnabrück, Wolfsburg, Göttingen, Salzgitter, Hildesheim, mainly situated in its central and southern parts, except Oldenburg.
Lower Saxony is the only ' that encompasses both maritime and mountainous areas. The northwestern area of the state, on the coast of the North Sea, is called East Frisia and the seven East Frisian Islands offshore are popular with tourists. In the extreme west of Lower Saxony is the Emsland, an economically emerging but rather sparsely populated area, once dominated by inaccessible swamps. The northern half of Lower Saxony, also known as the North German Plain, is almost invariably flat except for the gentle hills around the Bremen geestland. Towards the south and southwest lie the northern parts of the Central Uplands: the Weser Uplands and the Harz Mountains. Between these two lie the Lower Saxon Hills, a range of low ridges.
The region in the northeast, the Lüneburg Heath ('), is the largest heathland area of Germany. In the Middle Ages, the town of Lüneburg was wealthy due to salt-mining and the salt trade. To the north the Elbe valley separates Lower Saxony from Hamburg, Schleswig-Holstein, , and Brandenburg. The left banks of the Elbe downstream Hamburg are known as the '''' (Old Country). Due to its gentle local climate and fertile soil, it is the state's largest area of fruit farming, its chief produce being apples.
Most of the state's territory was part of the historic Kingdom of Hanover, and the state of Lower Saxony has adopted the coat of arms and other symbols of the former kingdom. It was created by the merger of the State of Hanover with three smaller states on 1 November 1946. Provided by Wikipedia
1
Published 1976
“...Niedersachsen / Kultusminister...”
Book
2
3
4
5
Published 1953
“...Niedersachsen. Archivverwaltung...”
Serial
6
7
Published 1995
“...Niedersachsen / Innenministerium...”
Book
8
Published 2003
“...Niedersachsen / Landtag...”
Book
9
Published 1991
“...Niedersachsen / Landtag...”
Book
10
Published 1953
“...Niedersachsen. Archivverwaltung...”
Serial
11
12
Serial
13
Published 2009
“...Zeitgeschichtlicher Arbeitskreis Niedersachsen...”
Book
14
Serial
15
Serial
16
Published 1987
“...Die Künstlergilde, Landesverband Niedersachsen...”
Book
17
Published 1977
“...Niedersachsen Landtag CDU-Landtagsfraktion...”
Book
18
Published 1963
“...Pommersche Landsmannschaft, Landesgruppe Niedersachsen...”
Book
19
Published 1977
“...Niedersachsen / Minister für Bundesangelegenheiten...”
Book
20
Published 1975
“...Niedersachsen / Minister für Bundesangelegenheiten...”
Book